Silicon carbide refractory materials are widely used in various industrial applications due to their exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength. This article aims to provide an overview of silicon carbide and its applications in refractory materials.

1. What is Silicon Carbide?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound composed of silicon and carbon. It is known for its exceptional properties, including high thermal conductivity, excellent mechanical strength, and low thermal expansion. These properties make it an ideal material for refractory applications.
2. Refractory Materials:
Refractory materials are substances that can withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions without undergoing significant physical or chemical changes. They are commonly used in industries such as steel, ceramics, glass, and cement production. Silicon carbide refractory materials exhibit excellent properties that make them suitable for these applications.
3. Properties of Silicon Carbide Refractory Materials:
3.1 High Thermal Conductivity: Silicon carbide has a high thermal conductivity, which allows it to efficiently transfer heat. This property is beneficial in applications where temperature control is crucial, such as in furnaces and kilns.
3.2 Exceptional Mechanical Strength: Silicon carbide refractories possess high mechanical strength, enabling them to withstand mechanical stress and pressure. This property ensures the longevity and durability of refractory linings in various industrial processes.
3.3 Low Thermal Expansion: Silicon carbide exhibits a low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it expands minimally when exposed to high temperatures. This property is vital in refractory applications to prevent cracking or damage caused by thermal stress.
4. Applications of Silicon Carbide Refractory Materials:
4.1 Steel Industry: Silicon carbide refractories are widely used in steel production as linings for blast furnaces, ladles, and crucibles. They can withstand the extreme temperatures and corrosive environments encountered during steelmaking processes.
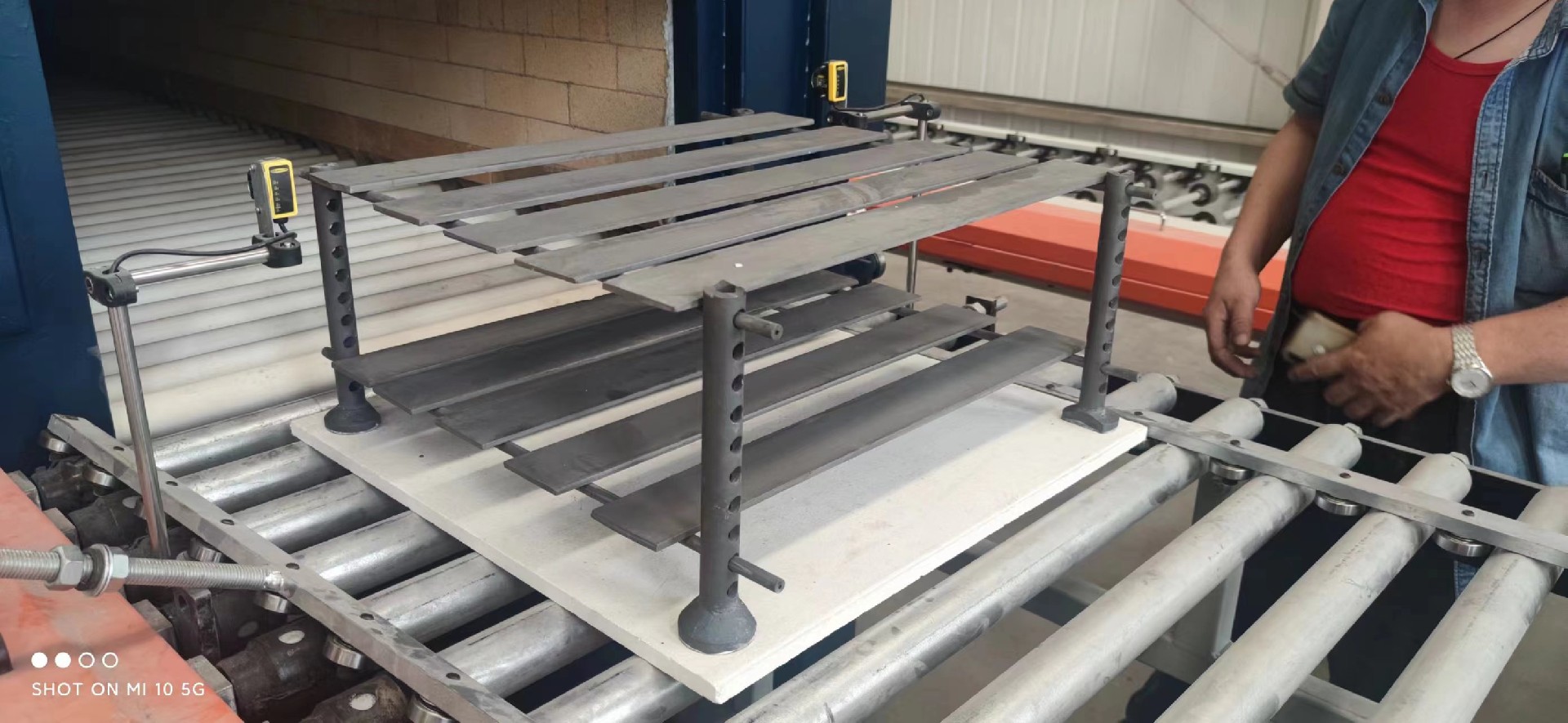
4.2 Ceramics and Glass Industry: Silicon carbide is used in the production of ceramics and glass due to its high thermal shock resistance. It is commonly used as kiln furniture, burner nozzles, and saggers in ceramic and glass manufacturing.
4.3 Cement Industry: Silicon carbide refractories find applications in the cement industry, particularly in rotary kilns and cyclone preheaters. Their high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical strength make them suitable for withstanding the abrasive and high-temperature conditions in cement production.
5. Conclusion:
Silicon carbide refractory materials offer exceptional properties that make them a preferred choice in various industrial applications. Their high thermal conductivity, exceptional mechanical strength, and low thermal expansion make them suitable for withstanding extreme temperatures and harsh environments. From the steel industry to ceramics and cement production, silicon carbide refractories play a vital role in ensuring efficient and durable operations.